One of the hardest parts of learning Deep Learning is just figuring out how to start! A particularly annoying part of the process is getting access to a GPU environment - GPUs aren’t absolutely necessary for learning DL, but they are an essential part of making problems feasible to solve in a reasonable amount of time, and it’s great to start with them from the beginning if you can.
In this post I’ll walk through adding a GPU node to our private network. Ideally we would build this from scratch so we can modify more easily as needed, but right now let’s just get started quickly with a pre-build AMI.
Deploy the Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
Amazon’s made things easy by pre-configuring a CentOS machine with all the necessary drivers and the most common DL libraries. We can browse to the Deep Learning AMI here
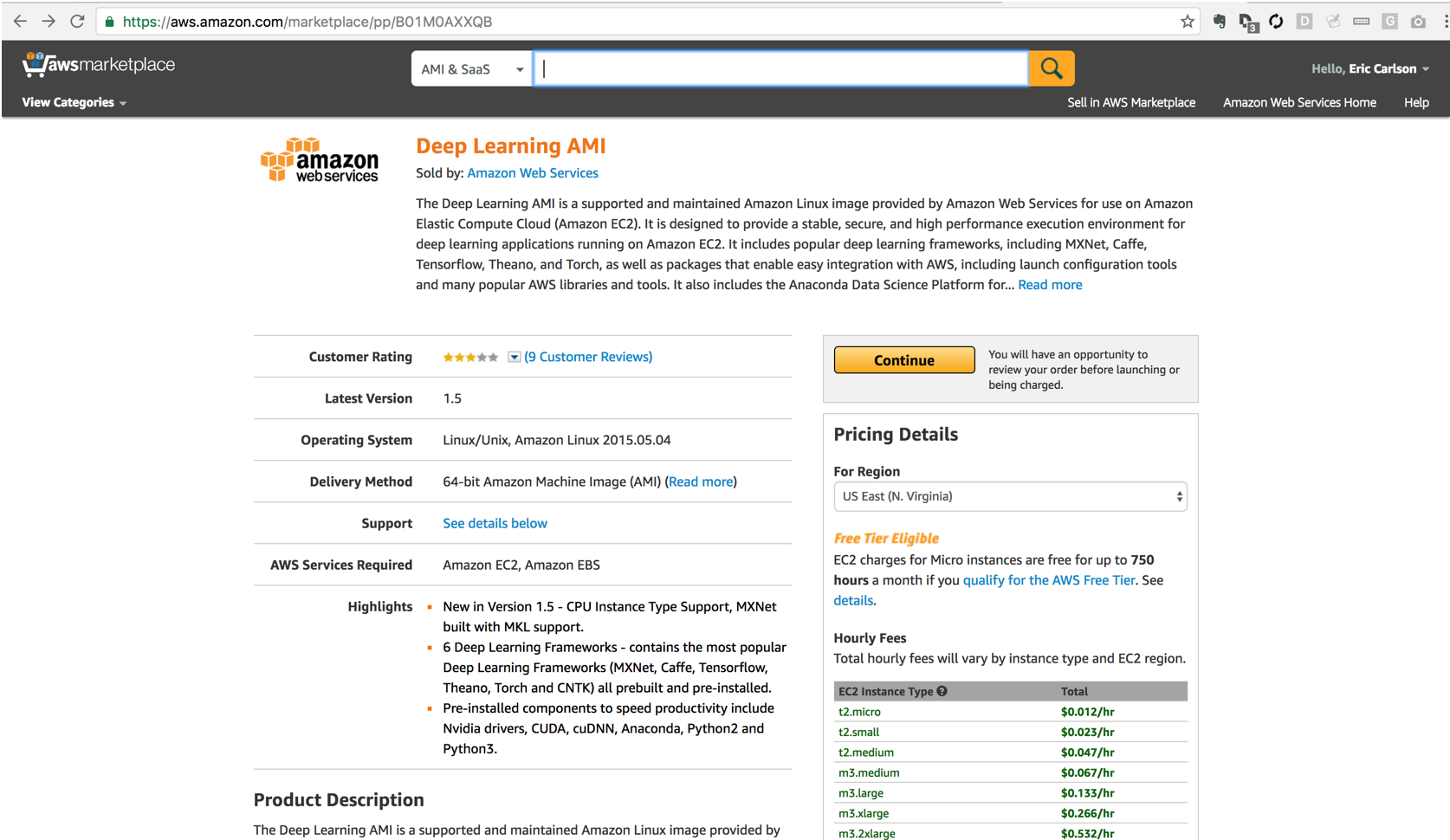 

Select continue to go on with configuration. The main things to select are:
- Region: US East (to match our previous cluster)
- Instance Type: p2.xlarge has a K80 GPU and sufficient processor for learning
- VPC: Select our VPC and subnet as configured previously
- Security Group: Select previously configured security group to allow access through bastion node
- Key Pair: Choose your ssh key
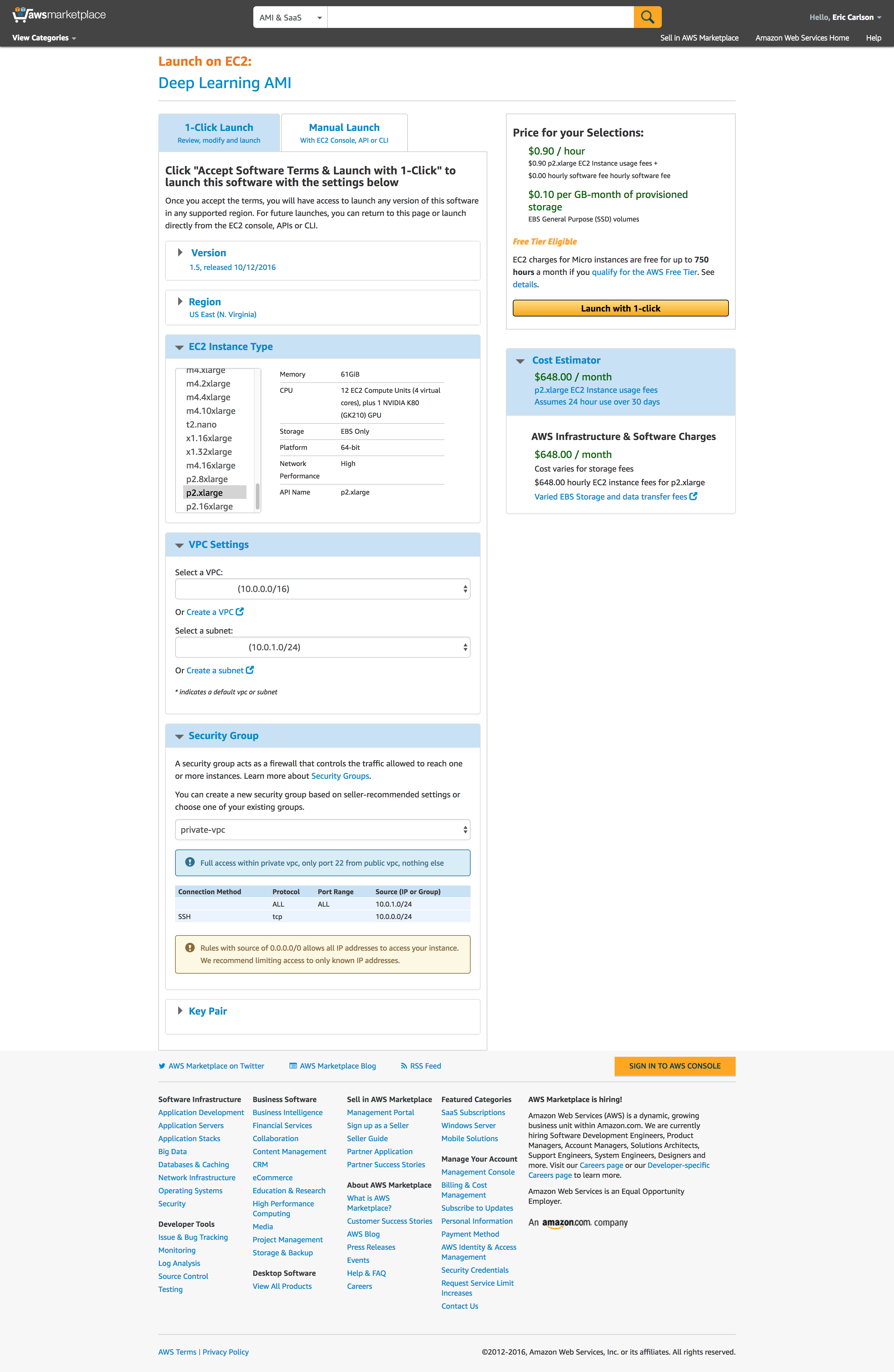 

Verify settings on confirmation page

And when you go to your console you should see the machine launching

Connect through our Bastion node and verify we see the GPU
ssh config:
Host panda-gpu
Hostname 10.0.1.127
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/xxx
User ec2-user
Now ssh to our instance
$ ssh panda-gpu
Update packages as needed
$ sudo yum update
Let’s see what we have…
$ lspci|grep -i nv
00:1e.0 3D controller: NVIDIA Corporation GK210GL [Tesla K80] (rev a1)
$ lsmod|grep -i nv
nvidia 8631809 0
$ nvidia-smi
Fri Dec 30 06:14:11 2016
+------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 352.99 Driver Version: 352.99 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 Tesla K80 On | 0000:00:1E.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 38C P8 27W / 149W | 55MiB / 11519MiB | 0% Default |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: GPU Memory |
| GPU PID Type Process name Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
NVidia K80 found, great!
Test with Python
Update some needed python packages, both 2.7 and 3.x
for installer in pip pip3; do
for package in pip ipython keras; do
sudo /usr/local/bin/$installer install --upgrade $package
done
done
Let’s test to make sure GPU is accessible from Python
$ ipython
In [2]: import tensorflow
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcublas.so.7.5 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcudnn.so.5 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcufft.so.7.5 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcuda.so.1 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcurand.so.7.5 locally
In [3]: %cpaste
Pasting code; enter '--' alone on the line to stop or use Ctrl-D.
from tensorflow.python.client import device_lib
def get_available_gpus():
local_device_protos = device_lib.list_local_devices()
return [x.name for x in local_device_protos if x.device_type == 'GPU']
:--
In [4]: get_available_gpus()
I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_gpu_executor.cc:925] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_init.cc:102] Found device 0 with properties:
name: Tesla K80
major: 3 minor: 7 memoryClockRate (GHz) 0.8235
pciBusID 0000:00:1e.0
Total memory: 11.25GiB
Free memory: 11.13GiB
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_init.cc:126] DMA: 0
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_init.cc:136] 0: Y
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:838] Creating TensorFlow device (/gpu:0) -> (device: 0, name: Tesla K80, pci bus id: 0000:00:1e.0)
Out[4]: ['/gpu:0']
Let’s also test with keras and theano
$ ipython
Python 3.5.1 (default, Sep 13 2016, 18:48:37)
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
IPython 5.1.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python.
? -> Introduction and overview of IPython's features.
%quickref -> Quick reference.
help -> Python's own help system.
object? -> Details about 'object', use 'object??' for extra details.
In [1]: import keras
Using Theano backend.
Using gpu device 0: Tesla K80 (CNMeM is disabled, cuDNN 5103)
/usr/local/lib/python3.5/site-packages/Theano-0.8.2-py3.5.egg/theano/sandbox/cuda/__init__.py:600: UserWarning: Your cuDNN version is more recent than the one Theano officially supports. If you see any problems, try updating Theano or downgrading cuDNN to version 5.
warnings.warn(warn)
If we want to use Python 2.7 for anything we need to modify ipython2 starter… (I found a bug)
$ sudo vi `which ipython2`
(change to 2.7, had been 2.6)
Can now test in 2.7
$ ipython2
Python 2.7.12 (default, Sep 1 2016, 22:14:00)
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
IPython 5.1.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python.
? -> Introduction and overview of IPython's features.
%quickref -> Quick reference.
help -> Python's own help system.
object? -> Details about 'object', use 'object??' for extra details.
In [1]: import keras
Using Theano backend.
Using gpu device 0: Tesla K80 (CNMeM is disabled, cuDNN 5103)
Connect to our NFS and existing user accounts
Now let’s connect to our nfs controller and setup a local user account
$ sudo yum install nfs-utils nfs-utils-lib
added to /etc/fstab:
10.0.1.6:/mnt/homes /mnt/homes nfs rsize=8192,wsize=8192,timeo=14,intr,soft 0 0
10.0.1.6:/mnt/data /mnt/data nfs rsize=8192,wsize=8192,timeo=14,intr,soft 0 0
us-east-1d.fs-cf17da86.efs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:/ /mnt/efs nfs rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,local_lock=none 0 0
Create mount points and mount
for d in /mnt/homes /mnt/data /mnt/efs; do
sudo mkdir $d;
sudo mount $d;
done
Now add my group and users
$ sudo groupadd -g 1500 users
$ sudo useradd -g users -d /mnt/homes/ecarlson/ -M -n -u 1500 ecarlson
Allow password-less sudo for ecarlson by adding to /etc/sudoers.d/ecarlson:
ecarlson ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
When logging in to this AMI it is assumed that files in ec2-user are accessible to configure the environment - change permissions:
$ chmod -R ugo+r /home/ec2-user
$ chmod ugo+x /home/ec2-user
Now, re-login as ecarlson, should be able to access everything. Changed .ssh/config to following:
Host panda-gpu
Hostname 10.0.1.127
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/xxx
User ecarlson
Note - need to specify system python, not anaconda…
$ export PATH=/home/ec2-user/src/torch/install/bin:/usr/local/cuda/bin:/usr/local/bin:/opt/aws/bin:/home/ec2-user/src/cntk/bin:/usr/local/mpi/bin:/home/ec2-user/src/caffe/build/install/bin:/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/opt/aws/bin
Run IPython to test
ecarlson@ip-10-0-1-221:~$ ipython
Python 3.5.1 (default, Sep 13 2016, 18:48:37)
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
IPython 5.1.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python.
? -> Introduction and overview of IPython's features.
%quickref -> Quick reference.
help -> Python's own help system.
object? -> Details about 'object', use 'object??' for extra details.
In [1]: %cpaste
Pasting code; enter '--' alone on the line to stop or use Ctrl-D.
from tensorflow.python.client import device_lib
def get_available_gpus():
local_device_protos = device_lib.list_local_devices()
return [x.name for x in local_device_protos if x.device_type == 'GPU']
:--
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcublas.so.7.5 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcudnn.so.5 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcufft.so.7.5 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcuda.so.1 locally
I tensorflow/stream_executor/dso_loader.cc:108] successfully opened CUDA library libcurand.so.7.5 locally
In [2]: get_available_gpus()
I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_gpu_executor.cc:925] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_init.cc:102] Found device 0 with properties:
name: Tesla K80
major: 3 minor: 7 memoryClockRate (GHz) 0.8235
pciBusID 0000:00:1e.0
Total memory: 11.25GiB
Free memory: 11.13GiB
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_init.cc:126] DMA: 0
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_init.cc:136] 0: Y
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:838] Creating TensorFlow device (/gpu:0) -> (device: 0, name: Tesla K80, pci bus id: 0000:00:1e.0)
Out[2]: ['/gpu:0']
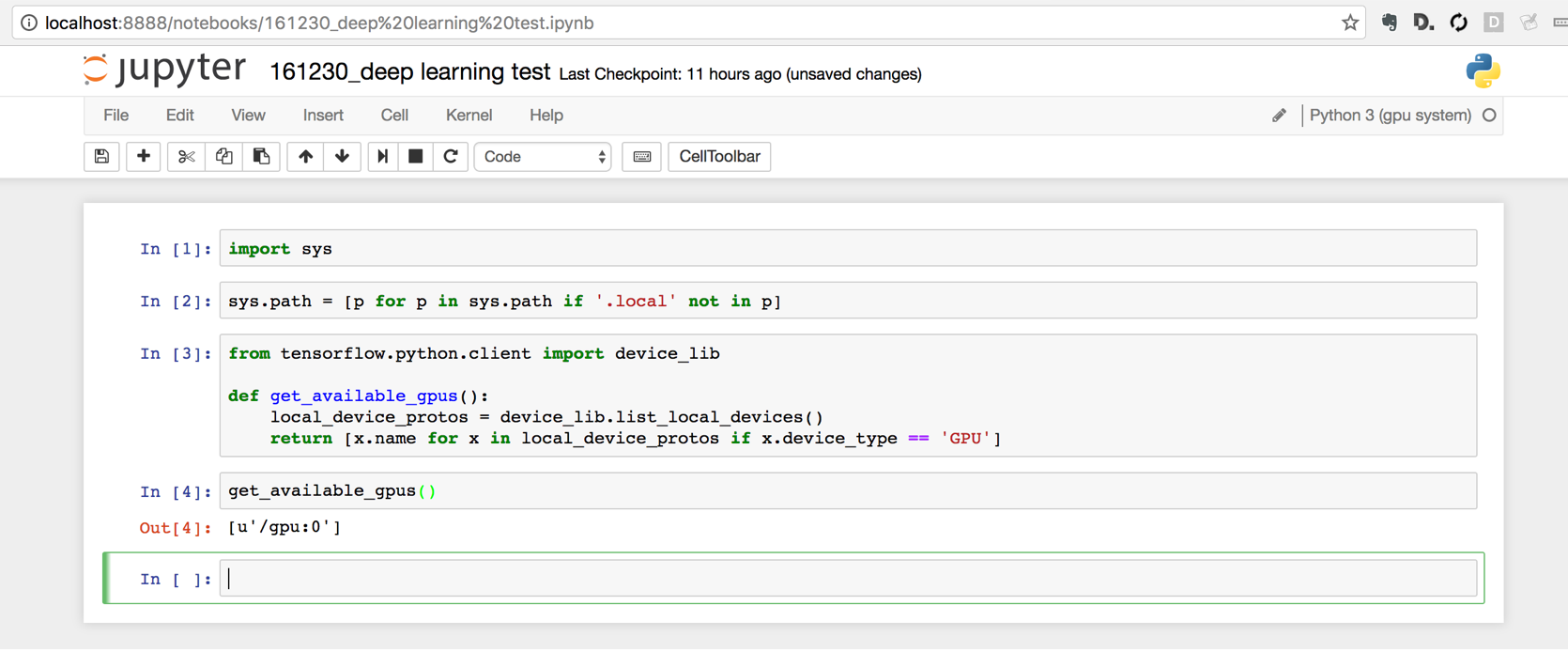
Access Jupyter Notebook
Now let’s try to get Jupyter Notebook working. First, setup a tunnel from our local computer
$ ssh -L 8888:localhost:8888 panda-gpu
Install the system python kernel to Jupyter
$ python -m ipykernel install --user --name gpu_system --display-name "Python 3 (gpu system)"
Now launch jupyter
$ jupyter notebook
Browse to localhost:8888
Note I had to remove ‘.local’ - numpy without gpu support was overriding the numpy on this system
 
Comments
comments powered by Disqus